The First Freedom: How We Lost Sight of Our Oldest Right—The Freedom of Movement
By Bashir Mobasher

Today, when we speak of migration, we no longer picture the awe-inspiring journeys of Herodotus, Xuanzang, Marco Polo, Ibn Battuta, or James Cook, men who ventured across oceans and deserts, through empires and unknown lands without needing a permit to enter and sometimes even received an audience with curious royalties.[1] We forget that their stories represent countless others, unnamed, unrecorded. We overlook the migration of the earliest human, homo erectus and homo sapiens, those bold crossings over mountains and plains, rivers and seas, islands and continents, by people who knew no boundaries, only the pull of necessity, survival, and discovery. They exercised the most ancient human freedom: the freedom to migrate.
Now, when we hear the word migration, our minds leap not to the journey, but to borders, passports, patrols, visas. We ask whether someone’s movement is legal or illegal, allowed or forbidden. We debate thresholds and quotas, risks and threats. Rarely do we ask the more human question: Does a person have the right to move freely? Doesn’t a person have the right to seek safety, pursue happiness, or simply adventure elsewhere?
What once seemed instinctive is now seen as impermissible, unnatural, even immoral. But this distorted view of movement is astonishingly new. It is newer than carriages and clocks, than spectacles and telescopes. For most of human history, the idea that one needed permission to move would have been absurd. Questioning human migration was questioning human nature—it still is. For over 90% of our existence as hunter-gatherers, humans were entirely dependent on movement.
Even with the rise of agriculture and the building of cities, migration between spaces remained natural to individual and social life. Entire communities shifted with the seasons. Trade and travel routes like the Silk Road, the trans-Saharan highways were arteries of constant movement. Nomadic peoples endured. Even the settled recognized migration as a response to drought, war, or opportunity. One needed no reason, or any reason would suffice.
This right to move is older than nearly all others. It predates the right to property, that most revered right in American political mythology. Property only became relevant when humans began to fence off land. Even the American settlers who enshrined property rights had to first migrate across oceans and continents to claim the land often by force. The right to the ‘pursuit of happiness’, enshrined in the US Declaration of Independence (1776), presupposes freedom of movement. Before there was freedom of speech, freedom of religion, the right to vote, or the right to due process, there was the right to migrate. Kings and empires might silence your tongue, outlaw your prayers, chain your thoughts, but they rarely questioned your decision to migrate. To migrate was beyond question. Often, it was the only freedom you could use to protect other personal rights by going to a new place. As the most respected freedom, it was the guardian of all other rights and freedoms.
Ancient thinkers, and traditions revered it as a sacred endeavour. Herodotus wrote, “Human prosperity never abides long in one place.” Aristotle saw migration as part of the natural order, while Socrates found it preceded new polities and civilizations. Religious traditions elevated migration into a moral duty: Abraham’s journey across deserts, the Exodus of the Israelites, the disciples’ missions across lands and cultures, and the Prophet Muhammad’s Hijra from Mecca to Medina were not mere detours or escapes. They were profound tales of faith, survival, and liberation in these traditions. Similarly, the Buddha’s Great Renunciation, the exiles in the Ramayana and Mahabharata, and the Anishinaabe migration were considered sacred journeys in these traditions shaping both the self and the world.
And yet today, that great engine of human history has been stalled. The rise of modern nation-states, colonial cartographies, and rigid immigration regimes has replaced this freedom with control. The invention of passports, visa systems, and surveillance bureaucracies has shackled what was once humanity’s most basic instinct. A species that roamed the earth for millennia now finds itself trapped inside boxes, walled by citizenship papers, embassies, fences, and checkpoints.
Ironically, it was the very colonial powers who once championed expeditions, economic and political adventurism, and settlement expansion that later rebranded rather more peaceful and kinder versions as a threat. The same empires that moved freely across oceans and continents in search of resources and dominion turned around to criminalize movement when it came from the margins. They eagerly promoted a pantheon of liberal rights, including free speech, religion, property, and even humanitarian intervention, but withheld the most ancient and universal of them all: the freedom of movement.
When the Universal Declaration of Human Rights was adopted, freedom of movement was included but subtly severed from the act of migration. A quiet sleight of hand. The right to leave was affirmed; the right to enter was not. It was a masterstroke of legal illusion, a political magic trick from the Western sleeve that has since cast a spell over global consciousness. A disillusion so complete, we forgot that the right to move was indeed the right to migrate; and it was never theirs to define, give or take. It was ours all along.
They even manufactured some baseless rights like preemptive self-defence, preemptive strikes, trade liberalization, and economic embargo, but somehow framed the right to migrate as too unrealistic, too disruptive, too dangerous to recognize. Denying the right to free movement has never been merely a matter of security or order; it reflects much deeper structural concerns. Facilitating and even coercing the flow of capital and resources from the Global South while restricting the movement of people ensures that global inequality remains entrenched, locking entire populations into structural disadvantage. These deeply embedded, often racialized, immigration systems have historically privileged certain regions and populations over others.
This redefinition has traveled far beyond its Western origins. For example, it is not only the United States or Germany that now deport Afghans, the very people they once claimed to protect. So too does Pakistan, Iran, and Tajikistan, who call Afghans their ‘Muslim brethren’, their ‘cultural kin’, their ‘linguistic neighbours’. Yet all these words evaporate at the border. Solidarity collapses at the gate.
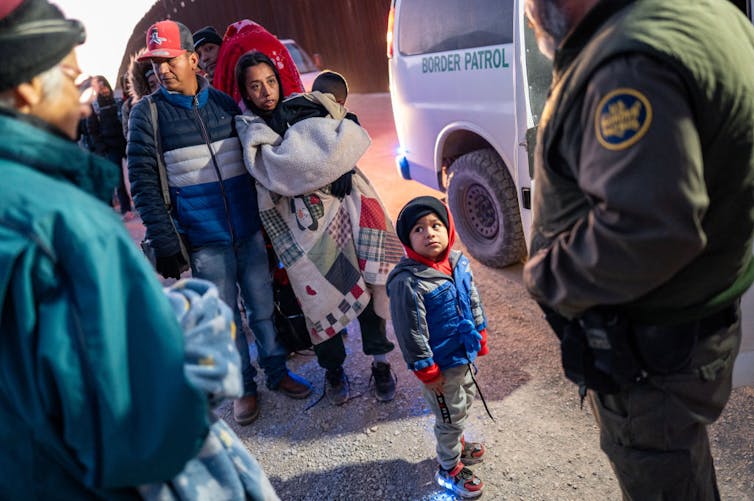
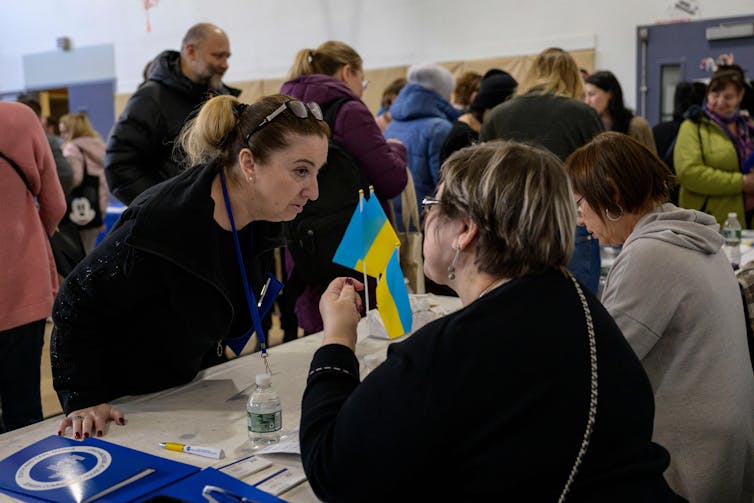
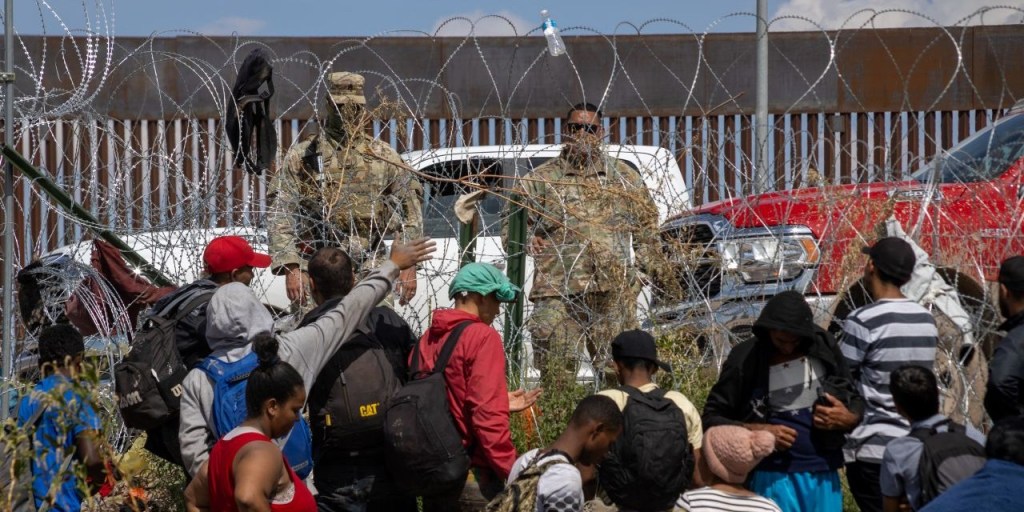
Today, we no longer speak of migration as a right. We speak of it as a problem. A crime, a disruption to be managed. The image of the migrant has shifted from that of a seeker or survivor to that of an invader. We no longer greet them with wonder. We do not ask about their journeys, their struggles, their dreams. We fear them. Our attention has shifted from people to policies, from humanity to geography. We have created a world where those most in need of movement are the most forbidden to move. People are trapped in war zones, failing economies, and ecological disasters, not because they cannot escape, but because they are not allowed to. The powerful still glide across borders with ease; the vulnerable are held hostage by the coordinates of their birth. Worse still, this system has seeded hatred and xenophobia, nationalism, and exploitation. It has enabled trafficking where safe passage is denied. It has weaponized difference and built moral hierarchies out of geography. Borders are no longer lines; they are Great Walls of China, dividing people, excluding them.
To forget this freedom is not only to forget our past; it is to endanger our future. In boxing humanity into artificial lines, we have betrayed the very idea of freedom. We have turned a natural preservation instinct, a birthright, into a crime. We have silenced the journey. And in doing so, we have not only lost sight of our first freedom; we have lost a piece of what it means to be human.
[1] The empires were, however, hesitant to let Ibn Battuta and Marco Polo leave because they needed their services, not because they had some random law about migrations.
Dr. Bashir Mobasher teaches at the American University (DC) Department of Sociology, New York University DC, and the American University of Afghanistan Departments of Political Science. Dr. Bashir is the current President of Afghanistan Law and Political Science Association (in Exile). He is an expert in comparative constitutional law, identity politics, and human rights. He has authored, reviewed, and supervised numerous research projects on constitutional law, electoral systems, and identity politics. His recent research projects are centered around decentralization, social justice, and orientalism. Bashir obtained his B.A. (2007) from the School of Law and Political Science at Kabul University and his LLM (2010) and PhD (2017) from the University of Washington School of Law.