The Taxing Debate on Migration in the U.S.
By Mary Capone
November 19, 2024
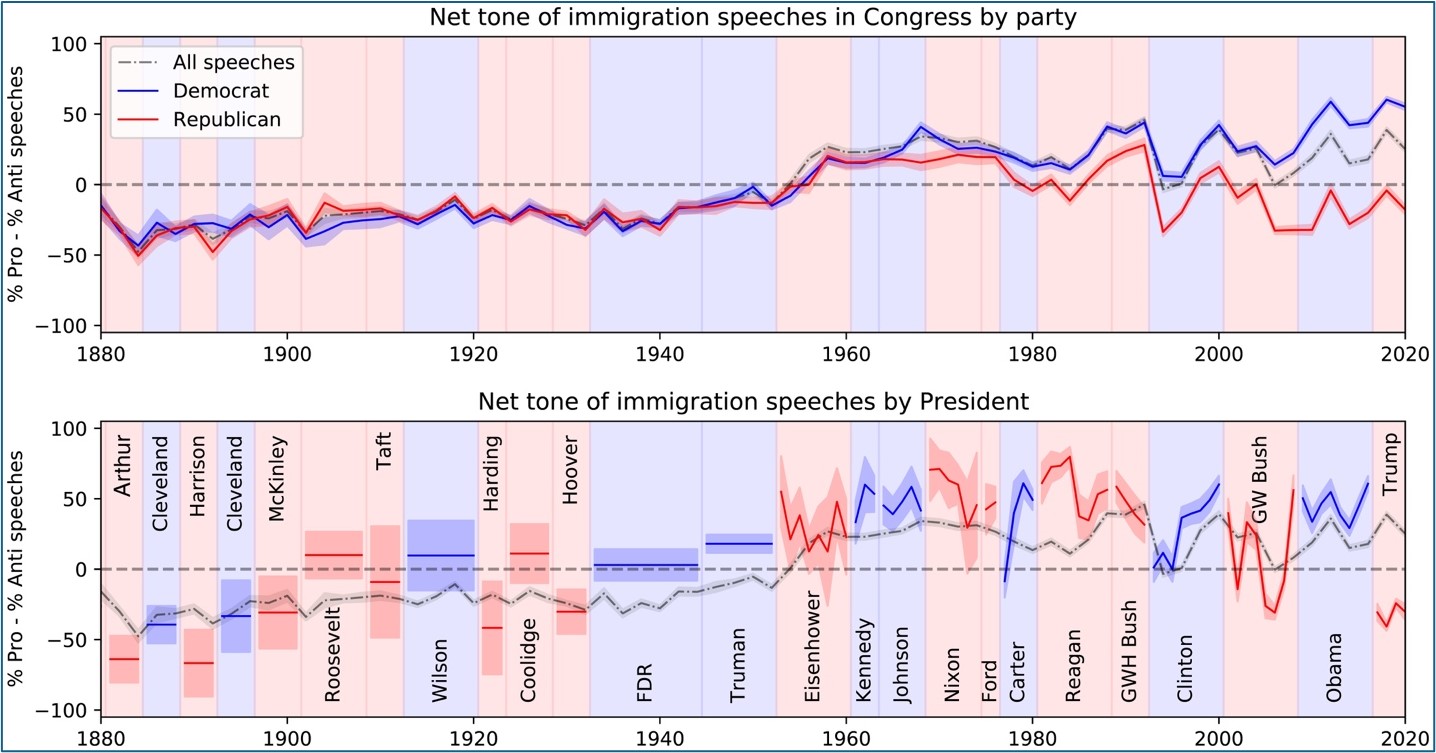
Nearly half of American adults feel that immigration threatens national identity. This proportion has increased in recent years as anti-immigration sentiments have surged in politics and partisan divergence has deepened in rhetoric. The former Trump administration was highly influential in the anti-immigration movement, with much of Trump’s campaigns hinging on xenophobic policies like building a wall on the southern border and ending DACA. Such policies jeopardize the human rights of immigrants in the United States, who make up nearly 14% of the U.S. population. The Biden administration’s handling of immigration has also been criticized by 60% of Americans, indicating that the ongoing conflict over immigration is worsening.
Polls from PBS NewsHour, 2024.
Why is migration so controversial? Shouldn’t people be allowed to migrate safely?
The answer lies in white supremacy and ‘tax dollars.’
At a 1983 Conservative Party conference, former UK Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher famously said, “If the State wishes to spend more, it can do so only by borrowing your savings or by taxing you more. It is no good thinking that someone else will pay—that ‘someone else’ is you. There is no such thing as public money; there is only taxpayers’ money.” Like many politicians, Thatcher propagated the notion that government spending relies on taxpayers’ money, placing the burden of spending on individuals.
Similar sentiments are not uncommon in the United States. Former Republican governor of Wisconsin, Scott Walker, featured this tagline in his 2018 campaign targeting his opponent: “Tony Evers: Special treatment for illegals, higher taxes for you.” Donald Trump continues to campaign on anti-immigration policies to appeal to Americans who feel skeptical about their tax dollars going to immigrant welcoming programs. Trump’s campaign website highlights “20 Core Campaign Promises to Make America Great Again,” two of which focus on blocking immigration, including the first promise: “Seal the border and stop the migrant invasion.” These arguments are used to justify relatively small government investment in important services that benefit communities of color and immigrants by suggesting they would be an imposition on the ‘taxpayer.’
To understand the historical use of the term ‘tax dollars,’ Camille Walsh analyzed hundreds of letters defending racial segregation addressed to the Supreme Court in the years following the ruling in Brown v. Board of Education (1954). One-third of the letters consisted of some language about taxes, taxpayers, or having “paid” for public schools, implying the right to decide whether to keep them segregated. The American ‘taxpayer’ historically represents white individuals, and such language “obscured class divisions among whites and elevated those racialized groups presumed to have higher taxable income to a higher position in claiming citizenship rights.” White individuals like Aura Lee (1956), argued that “poor white taxpayers are entitled to enjoy some all-white places, if they so desire.”
As the term ‘taxpayer’ is historically associated with whiteness, it is used to justify the entitlement of resources concentrated in white communities. Meanwhile, the ‘nontaxpayer’ is meant to symbolize Black and Brown individuals who are perceived not to have “earned” their rights. While this argument is used to exclude people of color from resources, historian James Anderson finds that taxes from predominantly Black communities were at least as much during the time of the Brown ruling, and often higher than those of white neighborhoods. These taxes were often distributed by white school boards into all-white schools prior to Brown. This does not account for today’s common tax evasion of the nation’s wealthiest individuals and corporations. The Treasury Department estimates that there is a $160 billion gap between what the wealthiest 1% of the population should pay and what they actually pay.
Seventy years after the ruling in Brown v. Board of Education, politicians, citizens, and the media hold ‘taxpayer dollars’ to be sacred. Similar to the discussions surrounding racial integration in the mid-20th century, immigration represents a battle between the ‘taxpayer,’ or white American, and the ‘nontaxpayer,’ or immigrant. Just as white parents feared sending their children to integrated schools with “much lower standards and run-down facilities than the ones that [they] helped pay for,” many white Americans do not want immigrants to have access to vital resources and fear the use of their dollars on government spending.
Nevertheless, between sales taxes and property taxes, undocumented immigrants pay billions of dollars in taxes each year. Not only are immigrants taxpayers, but they pay taxes at higher rates than the richest Americans and get less in return. Taxpayer rhetoric is another weapon of othering by separating white U.S.-born individuals from Black and Brown immigrants, regardless of who pays their taxes.

Graph from the American Immigration Council (2016).
A quote from former Chair of the U.S. Federal Reserve Alan Greenspan counters concerns about government spending causing a deficit, stating: “There is nothing to prevent the government from creating as much money as it wants.” Similar to banks not lending out depositors’ money, government spending does not use tax dollars for spending. To illustrate this, the U.S. government spent trillions on wars post-9/11 and hundreds of billions to bail out banks in 2008, neither of which were framed as a tax dollar problem. Despite the framing of funding essential services as an attack on individual taxpayers, in reality, it falls within the bounds of federal government spending.
International law considers migration to be a universal right. Immigration control “is a relatively recent invention of states,” according to Vincent Chetail, a professor of international law. The U.S. has a duty to protect the rights of all people and not discriminate based on race, national origin, religion, or any other group category according to the 14th Amendment, and many international treaties it is a party to.
Research indicates that government investments in immigrants have a higher return over time. For example, more educated immigrants earn more and, therefore, pay more in taxes. Fiscal concerns are not based on reality, as immigrants are net contributors to the federal budget. ‘Tax dollars’ are simply a code for white dollars to instill fear and discrimination against vulnerable populations, despite taxation realities.
Mary Capone is a researcher at the Immigration Lab at American University.
You can republish and reprint this piece in full or in part as long as you credit the author and link to the original when possible.