By Anjini K. Patel
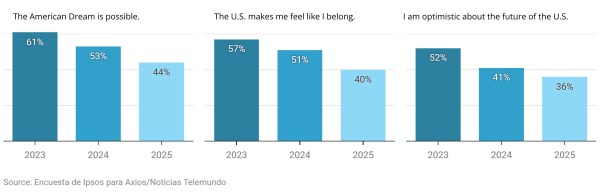
A recent Telemundo survey reveals increasing pessimism from Latinos in the United States regarding their sense of belonging. Telemundo, in collaboration with Axios and Ipsos, surveyed a nationally representative sample of over 1,100 U.S. Latino adults from October 21 to 27, 2025. Conducted in both English and Spanish, the survey asked a variety of questions about their views on the American Dream, their sense of belonging in the US, and their optimism about the future of the country. Only 44% of respondents described the American Dream as achievable in 2025, a decrease from 61% in 2023. Similarly, 40% of 2025 respondents affirmed that the US makes them feel like they belong, and only 36% felt optimistic about the future of the US. This compares to 57% and 52%, respectively, in 2022. This survey provides an insight into the feelings of Latinos as they navigate the uncertainty of the current American political landscape.
The survey also asked respondents about their anxieties related to being Latino/Hispanic in the United States. Compared with 39% in June 2022, 53% of respondents in 2025 reported feeling worried about themselves or a loved one being attacked because of their ethnicity. Two out of three (2/3) Latinos who identify as Republicans say it is a good time to be a Latino in the United States, while only one in ten (1/10) Latino Democrats agree. Seventy-one percent (71%) of those aged between 18 and 29 and 57% of those who are 50 and older, said it is a bad time to be Latino.
Most respondents indicate that the Democratic Party, as compared to the Republican Party, better represents Latinos, cares more about them, and is better on economic and immigration policy. Additionally, most respondents agreed that the Republican Party takes Latino Americans for granted (39%) as compared to the Democratic Party (22%). Interestingly, more respondents describe the Republican Party as a good option for public safety compared to the Democratic Party, even in the face of increased fear and anxiety over being attacked for being Latino.
What do experts say?
Dr. Ernesto Castañeda, Director of the Center for Latin American and Latino Studies at American University, discussed this survey on Telemundo. As he states, the data from this poll are unsurprising given the very strong anti-immigrant rhetoric that Donald Trump and the Republican Party campaigned with and continue to use. Rather than focusing on people with violent criminal records, ICE raids and subsequent deportation, often without due process, have detained and deported people with all types of immigration statuses, and thus increased fear among Latinos. Castañeda points to comments by Justice Cavanagh and decisions by the conservative majority in the Supreme Court that made detaining someone based on their appearance and manner of speaking permissible, further blurring the lines between individuals with papers and those who are undocumented. In light of these violent mass deportations and detentions happening in public places, following stereotypes and racial profiling, it is no wonder that many Latinos report a decreased feeling of belonging in the United States.
Regarding the impacts of these recent events, Dr. Castañeda explains that the feasibility of immigrants achieving the American Dream is decreasing. While people still arrive in the United States with high hopes that “they can come and work hard, send remittances, enjoy a better life, and that their children can go to university, in the United States right now, we see high underemployment rates, and many people are afraid to go to work because of mass raids. We are seeing inflation. It is harder to pay for health insurance, housing, and to save.” In this way, the American Dream is stalled. Since the end of the pandemic, the U.S. had seen a rapid and strong economic recovery, which Dr. Castañeda attributes largely “to the people arriving, especially from Latin America, seeking asylum—Venezuelans, Cubans, Haitians, Nicaraguans, and others—which increased the US population by 1%, which was very significant.” With the border closing under the current administration and deportations by the dozens of thousands, businesses are unable to grow at the same rate. Dr. Castañeda underlines: “If there’s less migration, it doesn’t mean there will be more jobs for locals. It means there will be less work for everyone, and more people will lose their jobs because the demand for goods and services decreases, businesses cannot hire and grow, and therefore they stop hiring and start firing workers.”
Additionally, research shows that immigrants are much more likely to start businesses and hire more workers than businesses started by native-born citizens. Therefore, the lack of immigration has a negative impact on the overall economic growth of the United States. As Dr. Castañeda describes, “the fact that Latinos aren’t going to work here means there are fewer nannies. There are fewer construction workers, fewer lawyers, fewer nurses… it also makes many Latinos afraid. They don’t go to the markets, they don’t go to the malls, they are spending less, which has an impact, and many immigrants, seeing that there’s no American Dream anymore, aren’t going to bring their families or many of them are thinking about returning to their country.”
The decreased sense of belonging by the Latino/Hispanic community has affected numerous outlets that embrace these cultures. Some events honoring Hispanic Heritage Month were canceled. This hurt artists, folk dancers, and musicians, as well as the larger public, who did not have the opportunity to engage with these rich cultural traditions. “Latin restaurants are struggling,” Dr. Castañeda says. “Hundreds are closing because they can’t hire enough people; workers are afraid to go to work because food is so expensive. So, it’s no longer a profitable business for them. The decline of the Latino food business also means fewer dining options, fewer cultural spaces, and fewer opportunities for communities to enjoy Latino cuisine. This is a loss for the United States as a whole.”
Hope and Resilience in the Face of Uncertainty
How should the Latino community respond to the ever-changing political landscape in the United States? Dr. Castañeda urges people to “stay calm and continue with their daily lives. We often do this for our children and grandchildren, who, I truly believe, will have a good future. This storm is temporary. This will pass.” Importantly, he points out that nearly 80% of Americans view immigration positively. Mass raids are not popular, and vulnerable communities are witnessing peaceful protests carried out by citizens who are physically placing their bodies between immigration agents and migrants who are in the process of being detained. The November 2025 elections indicate that a majority of Americans reject the current administration’s extreme policies on immigration and the mismanagement of the economy. The anti-immigrant sentiment is driven primarily by the federal government under Donald Trump, not the American people. With a hopeful outlook, Dr. Castañeda says, “I think that once this nightmare is over, there will be a greater sense of belonging, so we have to have patience, have faith in your fellow citizens, and I do truly believe that this will pass and the future will be better for U.S.-born Latinos and those immigrants who are able to stay. There will be concrete actions that will tell Latinos that they belong because this is their home.”
Anjini K. Patel is a Sociology Research & Practice MA candidate at American University (AU) and works as a graduate research assistant at the AU Inequality, Social Justice, & Health Lab. Her research interests include immigration, criminal legal system & housing justice, and artivism & community building.











