Robert Albro, Associate Director, Center for Latin American and Latino Studies, American University
Fulton Armstrong, Research Fellow, Center for Latin American and Latino Studies, American University
Philip Brenner, Emeritus Professor of International Relations and History, American University
William LeoGrande, Associate Vice Provost for Academic Affairs and Professor of Government, American University
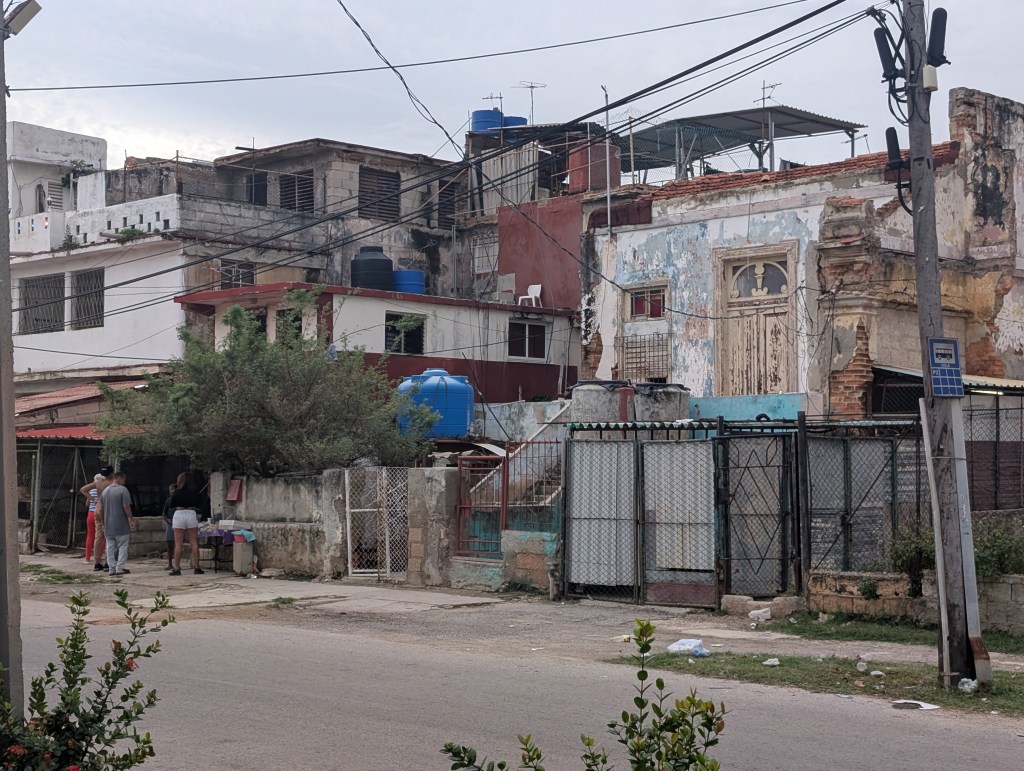

“A block in the Vedado neighborhood of Havana, Cuba.” Source: Robert Albro
In 1992, veteran Miami Herald journalist Andrés Oppenheimer brazenly forecast the downfall of the Cuban government. He reportedly asked Simon & Schuster to rush Castro’s Final Hour into print because the collapse seemed imminent. In the wake of the U.S. abduction of Venezuelan president Nicolás Maduro and his wife Cilia, pundits are once again predicting that the Havana government’s days are numbered. Based on our research during a recent visit* to Cuba, we conclude that headlines echoing Oppenheimer’s prediction are wrong again.
The feeding frenzy has been fueled by President Donald Trump and Secretary of State Marco Rubio. Early in January Trump called Cuba a “very badly failing nation,” and later asserted that “Cuba looks like it is ready to fall.” Rubio remarked at Trump’s January 3rd press conference that “Cuba is a disaster…it’s in total collapse.” Sources tell us that the Trump team believes regime change will occur by the end of 2026: the deepening immiseration of the Cuban people will lead dissenting government officials or military officers to declare that it’s time for the country to become a capitalist democracy, and poof, as if by magic, it will happen. Exactly how is unclear. Recent reports say Washington does not actually have a plan to bring this about but is in search of someone to lead the rebellion. Meanwhile, the U.S. goal remains fixed on creating a humanitarian disaster in Cuba.
The electrical blackouts that have plagued Cuba for the past several years will certainly get worse as Trump maintains the current policy of blocking Venezuelan oil shipments to the island. The small increase in oil coming from Mexico is hardly enough to replace the reduced supply from Venezuela. Most of the Cuban population already is suffering from shortages of food, medicine, medical care, gasoline, and necessities that regular electrical power would provide, such as functioning water pumps, lights, and working refrigerators. U.S. sanctions – which include severe limitations on tourism, remittances, and most trade, as well as the financial straitjacket the Trump administration imposed without justification by placing Cuba on the State Department’s list of “State Sponsors of Terrorism” – are the major source of Cuba’s misery.
But the organization of Cuba’s economy also contributes to its dysfunction. Subsidies for inefficient state enterprises, regulations that discourage foreign investment, and limitations imposed on farmers and private sector companies stifle productive economic activity. Cuba imports roughly seventy percent of its food despite an abundance of arable land and supply of fish. In 2025 it purchased more than $300 million in agricultural commodities, such as frozen chicken, from the United States. Notably the government had to sell some of its precious Venezuelan oil to China to earn enough hard currency to continue that level of food importation.
Lists of proposed economic reforms circulate in Havana, but while proposals may have merit in theory, they rarely take into account the constraints—both economic and political—under which the government is operating. Cuba is trying to implement a macroeconomic stabilization program with almost no foreign reserves, an intensifying U.S. embargo, and no access to help from the World Bank or International Monetary Fund.
On prior trips to Cuba, we were dismayed that some Cuban officials expressed little recognition that Cubans were becoming desperate and the government was facing a crisis of legitimacy. But in December we found this attitude had changed. The change became evident earlier in the year when President Miguel Díaz-Canel fired the Minister of Labor and Social Security for denying that there were real beggars looking for food in trash bins. Now there seems to be a sense of urgency, a recognition that the Cuban regime can no longer survive by muddling through.
Shortly after we arrived, the Communist Party took the unusual step of canceling the party congress scheduled to convene in April. In the past, party congresses have been the venue for announcing major reforms, so the reason for the cancellation became the focus of widespread speculation. One explanation we dismissed was that under the circumstances, the cost of bringing and housing so many delegates would be prohibitive or at least unseemly. Three other explanations struck us as more plausible. One was that party leaders were still arguing over which economic reforms the government should make. A congress that did not announce major changes would demoralize the population even further. A second explanation was that popular discontent was so great the leadership feared a convocation of grassroots party delegates might produce harsh criticism of the leadership’s handling of the crisis. A third, about which several of us are skeptical, was that national party leaders had reached consensus on reform measures but felt a need to move swiftly rather than wait for four months to conduct the grassroots discussion that normally precedes a party congress.
In any event, it appears that serious economic change might actually occur this year. While we were there, the government took two steps it had long resisted: it legalized the use of U.S. dollars in retail sales and floated the Cuban peso against the dollar and various other foreign currencies. Frustrated with the lack reforms, Vietnam and China have made deeper cooperation contingent on change. With the loss of Venezuelan oil, Cuba will need to rely even more on its international friends and will need to make the reforms necessary to reassure them that Havana is a reliable economic partner.
Reforms are not the only reason the Cuban government is unlikely to collapse. Economic despair does not automatically generate an opposition movement capable of overthrowing the government. Foreign diplomats in Havana told us that they perceive organized opposition in Cuba is weaker today than at any time in recent memory. Spontaneous anti-government demonstrations are likely to continue. But without a sustained organization to channel discontent security forces will be able to contain occasional outbursts. Moreover, the “maximum pressure” policy of the Trump administration is having exactly the opposite of its intended effect. Even Cubans who freely criticize government policies and leaders told us they resent U.S. actions and statements they view as exploiting their current difficult conditions to humiliate and dominate them.
In short, President Trump is more likely to realize his commercial interests in Cuba by sitting down with the government to see what sort of a deal can be made rather than waiting for the government to collapse—something U.S. presidents have been anticipating ever since 1959.
*The authors traveled to Cuba this past December 14-19.