
by Jonathan Valenzuela
During President Trump’s first term (2017-2021), a variety of immigration policy changes were implemented, which contributed to a shift in migration from Central America away from the United States and towards Europe. Now, in his second term more extreme anti-immigration policies alongside the rollback of Biden-era practices, such as the ending of the CBP One app, similar shifts of destination countries for Central American immigrants may continue. In 2023, it is estimated that there are about 4.3 million Central American immigrants in the United States, and 323,000 Central American immigrants in Spain.
Migration of Central Americans to the United States and Europe began during the armed conflicts of the 80s and 90s. It marked the start of a migration pattern which has only continued to grow. The most recent wave of Central American migrants to Europe began with Nicaraguan women in the mid-2000s to the early 2010s.
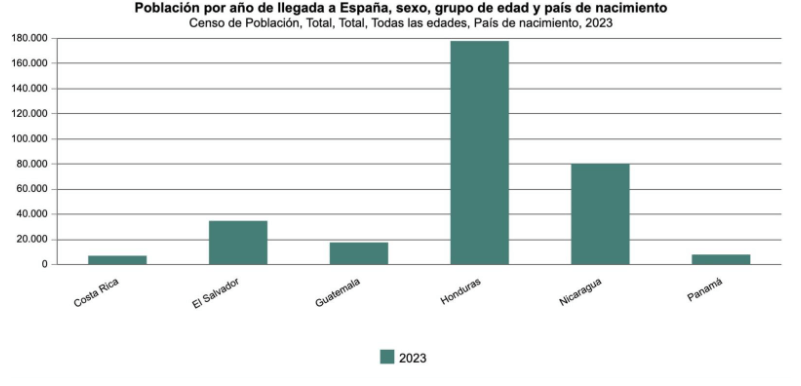
The largest Central American population is in Spain, with Hondurans most prevalent in Catalonia, Nicaraguans in the Basque Country, and Salvadorans in Madrid and increasingly in Seville. These populations have concentrated in these regions primarily because of established immigrant communities, strong labor markets, and an unmet need for labor in sectors such as elder or childcare. Notably, the population of Central Americans in Europe is composed primarily of Hondurans, Salvadorans, Guatemalans, and Nicaraguans. Costa Rican and Panamanian immigrants remain at a smaller number than those from the other four countries.
The outlook of Central American immigrants in Spain is both different and like those in the United States. On one hand, many female members of both communities work in domestic jobs such as childcare or housekeeping, but a main difference is that the Central American home in Europe is headed by the women of the household, who struggle less to find jobs than men do.
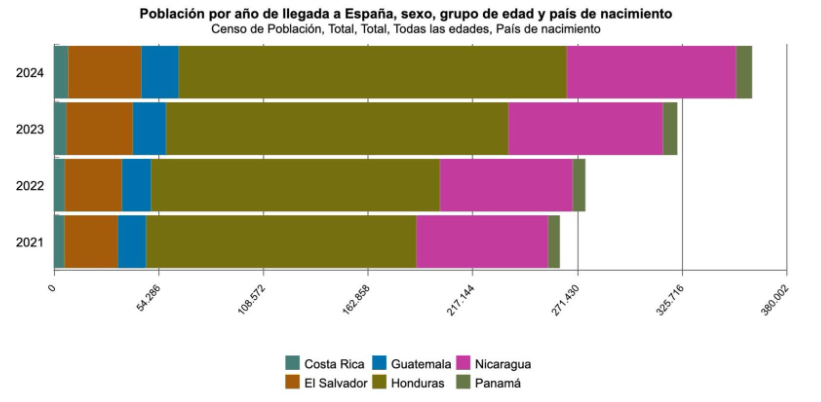
The acceleration of Central American immigration to Europe has notably grown because of the increased militarization of the United States’ southern border and policy changes since the first Trump administration. The increased difficulty of migrating to arrive to the United States made Central Americans seek other destinations. Spain is a solid option because of the ease of entering the country due to a lack of visa requirements, a perceived welcoming environment, an easier immigration process, a shared language, and similar cultural elements. From 2021 to 2024, the number of Central American immigrants in Spain grew by some 60,000.
The United States is the preferential destination for most Central American as it is the home of the largest diasporas. Experts agree that increased hostility on the Mexico-U.S. border, especially during the first Trump administration, is tied to the increase of Central American immigration to Europe. Through increased collaboration with Spain, the United States seeks to reduce the flows of immigration from the region towards itself, but not necessarily to stop it altogether.
Now, it is only a matter of time until this pattern further evolves with the second Trump administration, which has signaled its desire to further deter immigrants from entering the country. Regardless of the paid ads or policy changes the administration pushes, people will continue to immigrate.
Spain has continued to receive immigrants from Latin America and is considered to have “solved” immigration and it has the fastest growth of any European economy thanks to immigration. However, with anti-immigration protests in the country and throughout the world, the question remains whether these deterrent efforts will successfully push Central American immigrants to other destinations? And how long will these destinations such as Spain remain open to Central Americans before they decide to implement stricter migration policies as well? Or whether we are starting to see an equilibrium between the people needing to leave Central America, the people settling in other countries in the region, Mexico, the United States, and Spain, and the decrease in gang violence and economic opportunities in Central America.
Jonathan Valenzuela Mejia is a Guatemalan-American legal professional based in New York City. He completed a B.A. in Global Studies and a B.A. in Public Affairs with a minor in Central American Studies from UCLA.
Edited by Ernesto Castañeda, Director of the Immigration Lab and the Center for Latin American and Latino Studies.
